Prostate disease often occurs first in men of childbearing age. Their causes and types are different. The most common pathology is prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that the symptoms of prostatitis in men are latent for a long time.
What is the prostate in men?
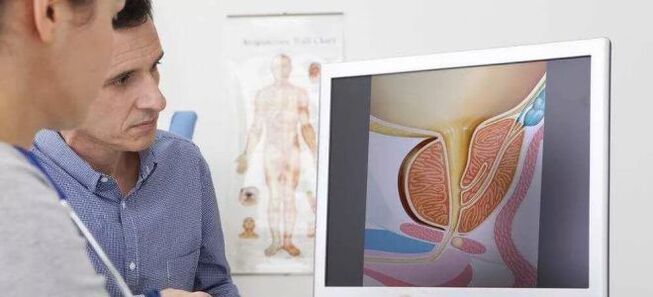
The prostate is an accessory sex gland in the male reproductive system. In shape it resembles a chestnut. The mass of the organ is in the range of 12–20 g. In its structure, the prostate resembles a sponge, which consists of many small cavities in which the secretion of the prostate gland is formed. During sexual intercourse, the secret enters the urinary tract through many tiny channels.
The body is divided into 3 zones:
- cranial;
- Average;
- Tail.
According to the observations of doctors, pathologies are mainly affected by the middle and tail zones. Neoplasms, malignant tumors are localized directly in them. Given these features, when pathology is suspected, specialists examine these areas of the prostate gland among the first.
Where is the prostate located?
With the onset of puberty, the male prostate becomes activated and begins to grow. This process is controlled by sex hormones. This androgen-dependent organ is located below the bladder. The first part of the urethra runs through the prostate. The ducts of the prostate open into the urethra.
If you look at the pelvis as a whole, you can say that the prostate is in the center. It encloses the bladder neck and the proximal urethra. The tip of the prostate touches the pelvic diaphragm, over which the external sphincter muscle of the urethra is located. Dorsally, the gland borders the ampulla of the rectum, through which digital examination of the prostate is often performed.
%20in%20a%20man.jpg)
What is the prostate responsible for?
The functions of the prostate are as follows:
- The production of fluid that makes up the liquid part of semen.
- Conversion of testosterone to its active form, dihydrotestosterone.
- The formation of the internal sphincter involved in urination along with the muscles of the bladder neck.
- Participation in the process of ejaculation.
Prostatitis - Types
Before emphasizing the main symptoms of prostatitis in men, it is necessary to consider the existing types of the disease. Inflammation of the prostate, depending on the form of the injury, the clinical picture is divided into the following types:
- Acute prostatitis- severe inflammation of the prostate, which develops as a result of bacterial infection.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis- characterized by a sluggish course, phases of exacerbation alternate with remission.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome- a difficult-to-diagnose form of prostatitis, manifested by constant pain in the pelvic area.
- Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis- does not have a pronounced clinical picture, is discovered by accident according to the results of a urinalysis.
- Granulomatous prostatitis- is considered a side effect of drug therapy for other diseases. Prostate tissue is gradually replaced by connective tissue.
Inflammation of the prostate - causes
Inflammation of the prostate in men can have various causes. However, in most cases they are associated with a careless attitude of the stronger sex to their health.
Among the factors provoking the development of pathology, doctors call:
- infections of the urogenital system;
- Circulatory disorders of the pelvic organs due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- prolonged absence of sexual relations, interrupted sexual intercourse;
- reduced local immunity;
- frequent hypothermia;
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
Infectious prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate of an infectious nature is a consequence of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the prostate. The process can proceed in acute or chronic form.
Provoking factors play an important role in the development of infectious prostatitis, including:
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- stressful situations;
- increased physical activity;
- bad habits (nicotine, alcohol);
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypothyroidism;
- HIV.
Non-infectious prostatitis
In most cases, chronic inflammation of the prostate is not contagious. Factors contributing to the development of this form of pathology are not fully understood.
Possible specialists include:
- irregular sex life;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- increased body weight;
- sedentary activity;
- constant stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- Constipation.

Signs of prostatitis in men and their symptoms
The symptoms of prostatitis in most cases go unnoticed for a long time. Periodic pain in the groin, a violation of sexual function, many men consider a temporary phenomenon. In 90% of cases, the development of inflammation of the prostate is manifested by a decrease in sexual activity, problems with ejaculation and difficulty urinating. In the acute form, the disease is accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being.
When an exacerbation of prostatitis occurs, the symptoms in a man are the following:
- increase in body temperature;
- general weakness;
- increased sweating;
- pain in the perineum, radiating to the anus and pubis;
- difficult urination.
The first symptoms of prostatitis
The first symptoms of prostatitis in men to look out for are sexual dysfunction. A man complains of a deterioration in erection or its complete absence. Ejaculation is also disturbed and the orgasm weakened. Similar symptoms of prostatitis in young men negatively affect sexual relations, so soon they avoid them so as not to fall into the eyes of their lovers. This leads to mental depression, constant tension and anxiety, which aggravates the situation.
Symptoms of prostatitis - what hurts?
Painful sensations in inflammation of the prostate appear mainly with the development of an acute form of the disease. Their localization may be different. So, back pain with prostatitis is resolved by about 50% of patients. In most cases, men experience excruciating pain in the perineum, scrotum, radiating to the sacrum.
The intensity of painful sensations can vary: from aching, uncomfortable sensations to pain that does not allow you to fall asleep at night. Increased pain can be noted during intercourse, with excessive sexual activity, and during ejaculation. These symptoms of prostatitis in men often appear among the first.
urination in prostatitis
Considering the inflammation of the prostate, the symptoms of the disease, among other things, doctors distinguish a violation of urination.
Patients often complain of the following nature:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- lack of empty bladder feeling after going to the toilet;
- difficulty urinating.
Characteristic manifestations:
- In most cases, it all starts with a man not being able to empty his bladder normally. The inflamed prostate increases in volume and gradually compresses the urethra.
- Progressive inflammation leads to the development of sclerosis of the bladder neck. As a result, the patient has frequent urges to go to the toilet.
- The chronic form is characterized by nocturnal urination: a man has to get out of bed in the middle of the night and go to the toilet.
- All this is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the groin area. Sometimes these are the only symptoms of chronic prostatitis.
Allocations for prostatitis
Regarding what symptoms can be observed with prostatitis, doctors also name discharge from the genital tract among the possible manifestations of the disease. The most common of these diseases is prostorrhea. It occurs with a decrease in the tone of the prostate and indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the gland. In such cases, the discharge occurs after urination or defecation.
The consistency of discharge from the genital tract resembles a thick, whitish-milky liquid. If, in addition to inflammation, infectious agents are present in the prostate, the color of the discharge changes to translucent with a yellowish tint. At the same time, the man notices severe discomfort in the anus and itching in the urethra.
Allocations are more often noted during the day after active movements when performing a prostate massage. Similar symptoms of prostatitis in men are forced to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Temperature for prostatitis
Acute inflammation of the prostate in men is always accompanied by hyperthermia. Body temperature with a similar disease often rises to 39 degrees.
A man notes the appearance of the following symptoms:
- sharp pains in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the perineum;
- pain when emptying the bladder;
- Discomfort and discomfort with bowel movements.
The temperature in most cases occurs only at the beginning of the inflammatory process. Over time, after taking antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs, normalization is observed. The lack of treatment and medical care at this stage is fraught with the progression of prostatitis and the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
Why is prostatitis dangerous?
Doctors recommend starting treatment with the appearance of the first clinical symptoms of the disease. To do this, a man must contact a urologist even if he suspects a disease. The consequences of prostatitis can be very diverse: from sexual dysfunction to conceiving problems and secondary infertility. The probability of developing such a pathology is 40% in the absence of adequate therapy. The most formidable complication is prostate adenoma - a malignant tumor.
Other negative effects are:
- anxiety disorder;
- Abscess;
- depression and apathy.